Connection
First, we need to create a connection with database:
import sqlite3
from sqlite3 import Error
def create_connection(db_file):
'''Create a database connection to a SQLite database'''
conn = None
try:
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_file)
print(sqlite3.version)
except Error as e:
print(e)
finally:
if conn:
conn.close()To create a connection, it's needed to invoke the function connect() from sqlite3, and save it in a variable.
In this case the connection was saved in conn, this variable will receive all the queries.
After running this on python3 interactive shell we will receive the version of sqlite library and the database will be generated:
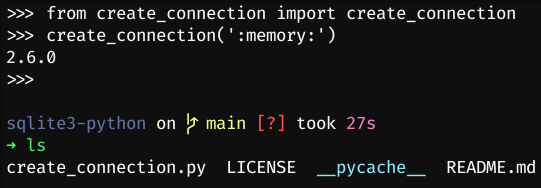
$ python3
>>> from create_connection import create_connection
>>> create_connection('my_database.db')
2.6.0
>>>
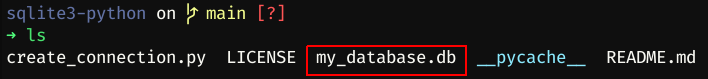
If you pass file name as ':memory:', the database will be saved on the memory of computer:
Refactor 1
Before of all, lets create a class where will contain all the methods:
db_manager.py
class DB_Manager:
def __init__(self):
self.conn = None
def create_connection(self, db_file="database.db"):
try:
self.conn = sqlite3.connect(db_file)
except Error as e:
print(e)Create tables
let's add the function create_table() to the class:
def create_table(self, create_table_sql):
""" create a table from the create_table_sql statement
:param conn: Connection object
:param create_table_sql: a CREATE TABLE statement
:return:
"""
try:
c = self.conn.cursor()
c.execute(create_table_sql)
except Error as e:
print(e)
With the DB_Manager, let's run the Python Interactive Shell:
$ python3Let's import the DB_Manager:
>>> from db_manager import DB_managerthen declare the variable containing the database name:
>>> database = 'pythonsqlite.db'then, declare the variable containing the SQL statement of project table and the task table:
>>> sql_create_projects_table = """ CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS projects (
id integer PRIMARY KEY,
name text NOT NULL,
begin_date text,
end_date text
); """
>>> sql_create_tasks_table = """ CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks (
id integer PRIMARY KEY,
name text NOT NULL,
priority integer,
status_id integer NOT NULL,
project_id integer NOT NULL,
begin_date text NOT NULL,
end_date text NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (project_id) REFERENCES projects (id)
); """then, we will instantiate the DB_Manager and create the connection:
>>> db_manager = DB_Manager()
>>> db_manager.create_connection()after, let's create the tables:
>>> if db_manager.conn is not None:
# create projects table
db_manager.create_table(sql_create_projects_table)
# create tasks table
db_manager.create_table(sql_create_tasks_table)
else:
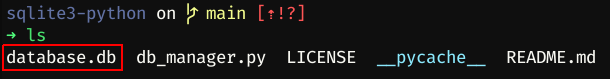
print("Error! cannot create the database connection.")If we run ls we will see that database.db was created:
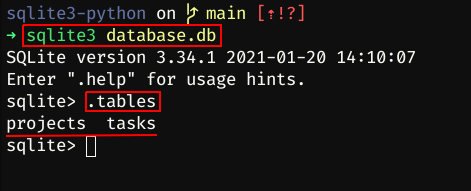
Now we can use the command sqlite3 passing our database as a param, then, run the .tables command to see the tables that we created:
Refactor 2
First, let's write the connection and the insert statement as a hard code on __init__ function:
# ...code
def __init__(self, db_file="database.db"):
try:
# create connection
self.conn = sqlite3.connect(db_file)
except Error as e:
print(e)
# create projects table
self.create_table(""" CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS projects (
id integer PRIMARY KEY,
name text NOT NULL,
begin_date text,
end_date text
);
""")
# create tasks table
self.create_table(""" CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks (
id integer PRIMARY KEY,
name text NOT NULL,
priority integer,
status_id integer NOT NULL,
project_id integer NOT NULL,
begin_date text NOT NULL,
end_date text NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (project_id) REFERENCES projects (id)
);
""")
# code...Then, delete the create_connection function.
Insert Data
To add data to the tables, we need the function execute of the Cursor object. The execute function receive two params, the sql statement and a tuple with the data, after this, we need to run the commit function of the connection, something like this:
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute(sql, data)
conn.commit()Let's create the function to add data on projects table and the tasks tables with this logic:
# ...code
def create_project(self, project):
""" create new project into the project table
:param conn:
:param project:
:return: project id
"""
sql = ''' INSERT INTO projects(name, begin_date, end_date)
VALUES(?,?,?) '''
cur = self.conn.cursor()
cur.execute(sql, project)
self.conn.commit()
return cur.lastrowid
def create_task(self, task):
""" create new task
:param conn:
:param task:
:return:
"""
slq = ''' INSERT INTO tasks(name, priority, status_id, project_id, begin_date, end_date)
VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?)'''
cur = self.conn.cursor()
cur.execute(slq, task)
self.conn.commit()
return cur.lastrowid
# code...Running the python3 interactive shell, import the class and instantiate it in the db_manager variable:
>>> from db_manager import DB_Manager
>>> db_manager = DB_Manager()after that, create the variable containing the project data, and a variable to save the project id on database:
>>> project = ('Cool App with SQLite & Python', '2021-03-20', '2021-03-23')
>>> project_id = db_manager.create_project(project)then, create two tasks and save it on the database:
>>> task_1 = ('Analyze the requirements of the app', 1, 1, project_id, '2021-03-20', '2021-03-23')
>>> task_2 = ('Confirm with user about the top requirements', 1, 1, project_id, '2021-03-20', '2021-03-23')
>>> db_manager.create_task(task_1)
1
>>> db_manager.create_task(task_2)
2The project and the tasks are saved now. Open the database to see the data.
With the open database, use this commands to format the output:
sqlite> .header on
sqlite> .mode columnUse the SELECT statement to get data from projects table:
SELECT * FROM projects;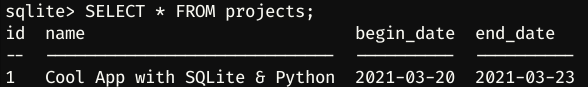
Use the same statement to get data from tasks table:
SELECT * FROM tasks;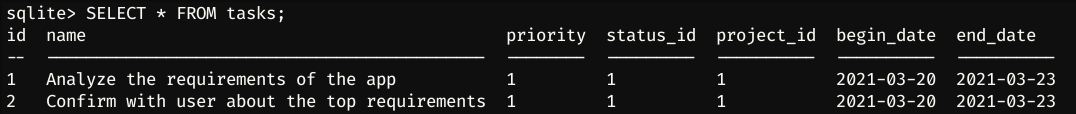
referencies:
SQLite Python: https://www.sqlitetutorial.net/sqlite-python/ [archive]
- Creating a New Database: https://www.sqlitetutorial.net/sqlite-python/creating-database/ [archive]
- Creating Tables: https://www.sqlitetutorial.net/sqlite-python/create-tables/ [archive]
- Insert data: https://www.sqlitetutorial.net/sqlite-python/insert/ [archive]